What is a Solar Panel and How Does It Work? A Complete Guide
Solar panels have become a cornerstone of renewable energy solutions, propelling the shift toward sustainable energy sources worldwide. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar energy capacity reached over 940 gigawatts globally by the end of 2020, indicating a dramatic increase in adoption due to decreasing costs and technological advancements. This shift is driven by a collective desire to reduce carbon footprints and reliance on fossil fuels, highlighting the critical role solar panels play in tackling climate change.
Understanding how solar panels operate is essential for both potential buyers and environmentally conscious individuals keen on maximizing energy efficiency. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells, a process that has seen significant improvements in efficiency and affordability. Reports from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) suggest that the average efficiency of solar panels has increased from around 15% in 2010 to approximately 20% in 2021, making them an increasingly viable option for homeowners and businesses alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of solar panels, offering insights into their functionality, benefits, and the transformative impact they have on our energy landscape.

What is a Solar Panel? Definition and Overview
A solar panel, commonly referred to as a photovoltaic (PV) panel, is a device that converts sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. At its core, a solar panel consists of numerous solar cells made primarily from silicon, a material that is highly efficient in capturing solar energy. When light photons hit these cells, they excite the electrons in the silicon, creating electron-hole pairs. This movement of electrons generates a flow of electricity, which can then be harnessed for various power needs.
In addition to individual solar cells, solar panels are typically encased in protective materials to enhance durability and performance. The arrangement of these cells, along with their ability to absorb sunlight efficiently, determines the overall efficiency and energy output of the panel. Solar panels are used in a variety of applications, from small residential rooftops to large solar farms, making them a versatile solution for harnessing renewable energy. As global awareness of sustainable practices grows, the implementation of solar panels continues to gain traction, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
Solar Panel Efficiency Comparison
The Science Behind Solar Energy: How it Works
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun's rays, transforming it into usable electricity through photovoltaic (PV) technology. At the core of solar panels are semiconductor materials, typically silicon, that absorb sunlight and release electrons. This process begins when photons from sunlight strike the solar cell, exciting the electrons and enabling them to flow through the material, creating an electric current. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar power accounted for approximately 3% of the total electricity generation in the U.S. in 2021, showcasing the growing adoption of renewable energy sources.
The efficiency of solar panels is a critical factor that determines their ability to convert sunlight into energy. Modern solar panels can reach efficiencies of over 20%, meaning that they convert more than one-fifth of the sunlight they receive into electrical energy. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reports that advancements in technology, such as the development of bifacial solar panels, which can capture sunlight on both sides, have the potential to increase energy output significantly and maximize the use of available space. This shift towards higher efficiency not only improves the viability of solar installations but also supports global efforts to transition to renewable energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Types of Solar Panels: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film
When exploring solar panels, it's essential to understand the different types available in the market: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Each type has distinct characteristics and applications, making them suitable for varying energy needs and installation environments.
Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency and longevity. They are made from a single crystal structure, which allows them to convert sunlight into electricity more effectively than other types. This results in a higher power output per square meter, making them a popular choice for space-constrained installations. However, they often come at a higher cost due to their manufacturing process and material quality.
On the other hand, polycrystalline panels consist of multiple crystal structures and are generally less expensive to produce. While they have a lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels, advancements in technology have significantly improved their performance. These panels are an excellent choice for large-scale solar installations where space is less of a concern. Lastly, thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, allowing for various applications, including building-integrated photovoltaics. They tend to have lower efficiency but can perform better in low-light conditions, making them suitable for specific environments. Each type of solar panel offers unique benefits, catering to diverse energy needs and budget considerations.
What is a Solar Panel and How Does It Work? A Complete Guide
| Type of Solar Panel | Efficiency (%) | Cost ($/W) | Lifespan (Years) | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline | 15-22% | $0.80 - $1.20 | 25-30 | Residential, Commercial |
| Polycrystalline | 13-16% | $0.70 - $1.00 | 20-25 | Residential, Commercial |
| Thin-Film | 10-12% | $0.50 - $0.80 | 15-20 | Large Scale, BIPV |
Components of a Solar Panel System: Key Elements Explained
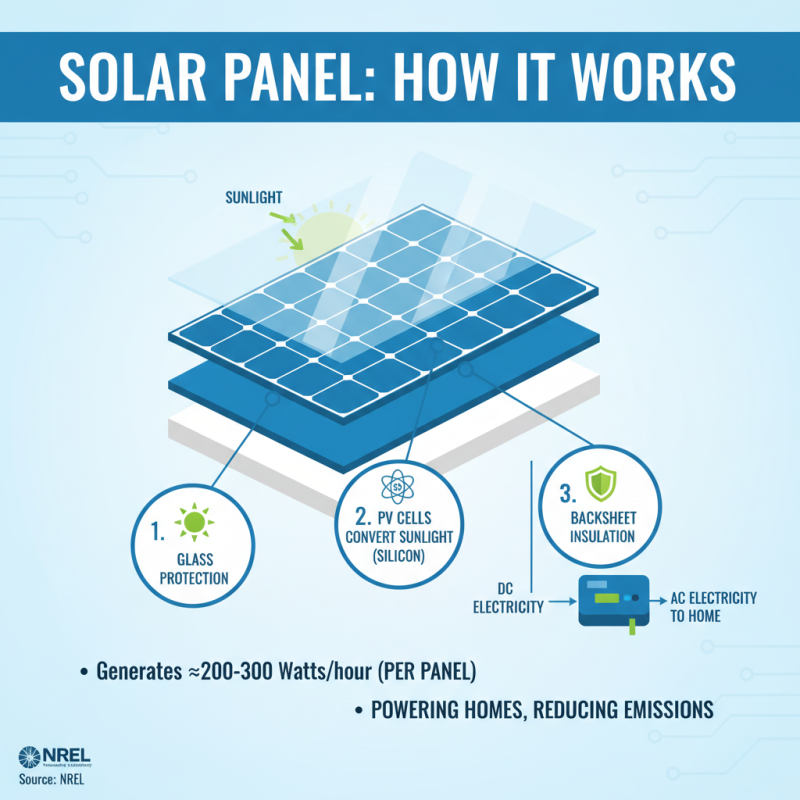
Solar panels are intricate systems composed of several key components that work together to convert sunlight into usable electricity. At the heart of any solar panel system are the photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are made of semiconductor materials—most commonly silicon. These cells capture solar energy and create a flow of electricity through the photovoltaic effect, which has the potential to generate around 200-300 watts per hour for a typical panel under optimal conditions, according to data from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
In addition to PV cells, a complete solar panel system includes an inverter, mounting structure, and in some cases, batteries. The inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the form of electricity that most household appliances use. Recent studies suggest that the efficiency of modern inverters can exceed 95%, improving the overall energy yield of solar systems. The mounting structure ensures stability and angle optimization for maximum sunlight exposure, while battery systems are used for energy storage, allowing households to utilize solar energy even during non-productive hours. Industry reports indicate that the global solar battery market is expected to grow significantly, indicating a rising demand for efficient energy storage solutions. Such components collectively make solar panel systems not only effective but also increasingly vital in the transition toward renewable energy sources.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Solar Panels for Energy Generation
The transition to solar energy has garnered significant attention due to its numerous benefits. One of the primary advantages of using solar panels for energy generation is their ability to harness renewable energy from the sun, which is abundant and inexhaustible. This leads to a reduction in reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a cleaner environment. Additionally, solar panels can significantly lower energy bills for households and businesses by providing a cost-effective way to generate electricity, especially in areas with high sunlight exposure.
However, there are challenges associated with the implementation of solar panel systems. The initial installation costs can be substantial, which may discourage some users despite the long-term savings. Moreover, solar energy generation is dependent on weather conditions and daylight hours, making it less reliable during cloudy days or at night unless supplemented with battery storage solutions. Maintenance and space requirements can also pose hurdles, as effective solar panel installations require adequate roof space or land and periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Balancing these benefits and challenges is crucial for individuals and organizations considering solar energy solutions.
Related Posts
-

7 Best Solar Panels for Maximum Efficiency in 2023
-
2025 How to Choose the Best Solar Panels for Your Home
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Solar Energy Panels for Home That Meet Your Technical Needs
-

10 Essential Tips for Sourcing Solar Panels Effectively in 2024
-

Advantages of Choosing the Best Solar Panels for Sustainable Energy Solutions
-

7 Compelling Reasons to Choose the Best Solar Panel for Home Energy Solutions